PROGRAM
With the launch of low-cost receivers with centimeter-class positioning engines, high-precision positioning applications are becoming more widely used in society, and positioning technology, which has been available only to a limited number of users, has entered a new phase of consumer-level products.
In the future, there will be a strong demand for human resources who can not only ensure the accuracy of positioning but also the reliability of positioning, countermeasures against deceptive signals and interference waves, and solve factors that prevent cm-class positioning by themselves. For example, when it comes to automotive driving support for cars, it is essential to ensure not only accuracy and convenience but also reliability, just like car navigation systems. In this project, we aim to produce human resources who can freely improve receiver mechanisms and positioning algorithms, which are the core of satellite positioning technology, to meet the above challenges.
In 2021, the faculty will prepare the program and teaching materials and start recruiting students. In 2022, the actual lectures using the program and teaching materials will be held for the equivalent of 15 x 90-minute sessions. The lectures will be held intensively in the summer when students have more time. This will be followed by practical training in an anechoic chamber at the Electronic Navigation Research Institute, and then we will work on developmental tasks and contests for the 2023 academic year.
SCHEDULE
| In 2021 | Prepare equipments and materials, and programs fo software GNSS |
| April of 2022 | Call for Participants |
| May 23, 2022 | Hold a meeting to explain “Software GNSS Receiver Program” seminar |
| August 8 – 10, 2022 (3days) | The 1st “Software GNSS Receiver Program” seminar |
| August 26, 2022 | The 1st Antenna Measurement |
| February 8 – 10, 2023 (3days) | The 2nd “Software GNSS Receiver Program” seminar |
| February 7, 2023 | The 2nd Antenna Measurement |
LEARNING MATERIALS
| 1 | Importance of learning Software GNSS Receivers |
| 2 | Overall GNSS system (3 segments) |
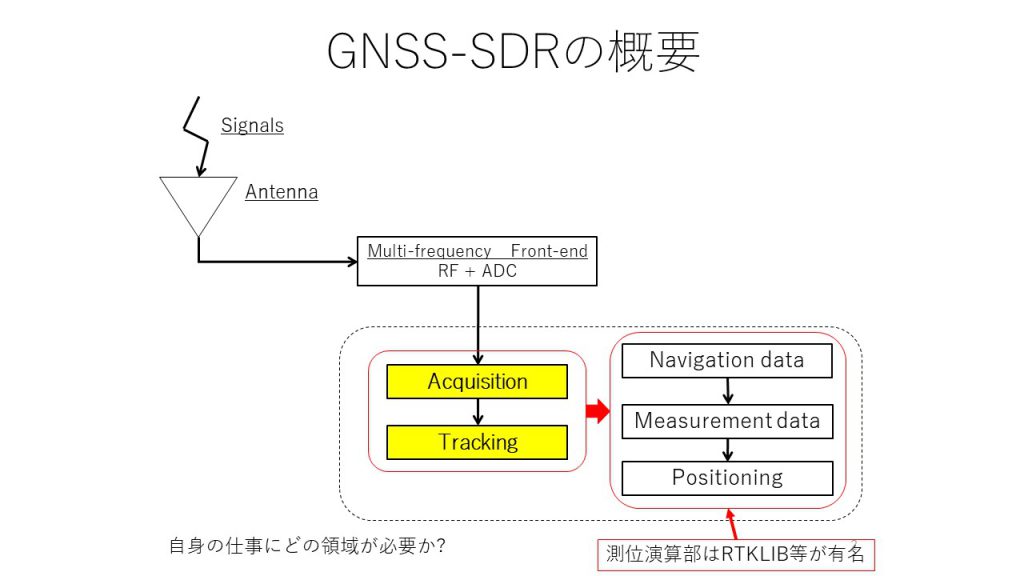
| 3 | GNSS receiver configuration (antenna, FE, signal processing, observation data section, positioning calculation section) |
| 4 | Roles & overview of Frontend (IF, bits, sampling, IQ values, etc.) |
| 5 | Introduction of software GNSS receivers used in teaching materials (Github, PC operating environment, etc.) |
| 6 | GNSS signals (knowing the signals from satellites) |
| 7 | Signal acquisition (importance of reacquire) |
| 8 | Signal tracking (DLL, FLL, PLL, signal strength, filter design, etc.) |
| 9 | Decoding navigation data |
| 10 | Generation of observation data and positioning operations |
| 11 | Utilizing FPGAs (HDL Basics) |
| 12 | Utilization of FPGA (generation of C/A code) |
| 13 | Roles & overview of GNSS simulator and anechoic chamber |
| 14 | Spaceborne receivers, lunar positioning, LEO satellites |
| 15 | Future GNSS and QZSS plans and expectations (also linked to developmental issues) |
SOFTWARE GNSS
As the name implies, it is possible to perform signal processing and positioning operations inside a GNSS receiver on your PC by purchasing or developing a device called a front-end, which is a device that takes in the high-frequency part of the signal processing and positioning operations that are performed inside a general GNSS receiver. For more details, please refer to the presentation materials.
In this section, we will first introduce the front ends that are available in our program or in our laboratory. In particular, we have purchased a lot of RTL, so you can already borrow them. Please contact Professor, Kubo if you need other front ends.
Frond Ends







